 16 February, 2024
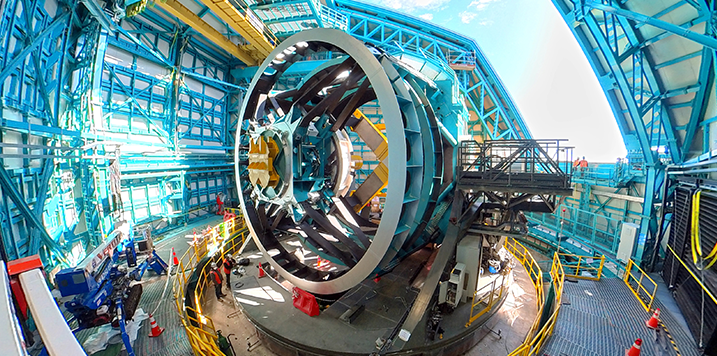
16 February, 2024The science industry today faces unprecedented challenges in its quest to unravel the mysteries of the universe and answer humanity's big questions. This endeavour has not only led to the discovery of phenomena such as the Higgs boson and the capture of the first image of a black hole, but has also led to the development of revolutionary scientific infrastructures such as CERN, the James Webb telescope, and the ITER reactor. In this context, Europe, with a budget of almost 40 billion euros earmarked for R&D in the coming years, and Spain in particular, stand out for their significant contribution and leadership in nuclear fusion and astrophysics projects.
Within this collaborative R&D ecosystem, where knowledge transfer between companies, universities and technology centres is vital, Tekniker emerges as a fundamental pillar in achieving technological advances for the Science Industry. This technology centre, with its deep knowledge in Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) and mechatronics, is at the forefront of the development of control, automation and connectivity systems for cutting-edge scientific facilities. Its efforts are materialised in innovative projects that aim to make scientific facilities more compact, efficient, autonomous, safe and sustainable.
Tekniker has demonstrated its ability to operate in extreme conditions through the design and automation of equipment such as those used in the Remote handling project for remote handling at the Swedish neutron source and the Muvacas facility, a test bed for nuclear fusion research. These projects illustrate how the centre combines its competences in design and automation to develop technologies that enable significant breakthroughs in critical fields.
Tekniker's work is not limited to automation and mechatronics. In the field of astrophysics, the centre has been instrumental in developing the software and control algorithms for the Rubin Observatory telescope, ensuring the exceptional motion accuracy needed for advanced astronomical research.This ability to design tailor-made solutions also extends to the advanced manufacturing sector, where Tekniker introduces emerging technologies such as lasers, additive manufacturing, and clean room processes, contributing to the improvement of manufacturability and competitiveness of companies.
In addition, Tekniker participates in projects aimed at improving the properties of materials and providing them with new functionalities, such as the development of smart coatings that prevent cold welding in satellite parts, demonstrating its commitment to innovation in space missions such as Solar Orbiter (SolO), ExoMars, and JUICE.
Tekniker's contribution to the Science Industry is a clear example of how collaboration between different actors in the innovation ecosystem can drive the development of advanced technological solutions, bridging the gap between scientific needs and the industrial fabric. With each project, Tekniker not only advances the frontier of scientific knowledge, but also strengthens the industrial capacity to face the challenges of the future.
 16 February, 2024The science industry today faces unprecedented challenges in its quest to unravel the mysteries of the universe and answer humanity's big questions. This endeavour has not only led to the discovery of phenomena such as the Higgs boson and the capture of the first image of a black hole, but has also led to the development of revolutionary scientific infrastructures such as CERN, the James Webb telescope, and the ITER reactor. In this context, Europe, with a budget of almost 40 billion euros earmarked for R&D in the coming years, and Spain in particular, stand out for their significant contribution and leadership in nuclear fusion and astrophysics projects.
16 February, 2024The science industry today faces unprecedented challenges in its quest to unravel the mysteries of the universe and answer humanity's big questions. This endeavour has not only led to the discovery of phenomena such as the Higgs boson and the capture of the first image of a black hole, but has also led to the development of revolutionary scientific infrastructures such as CERN, the James Webb telescope, and the ITER reactor. In this context, Europe, with a budget of almost 40 billion euros earmarked for R&D in the coming years, and Spain in particular, stand out for their significant contribution and leadership in nuclear fusion and astrophysics projects.